Types of LPS
Three types of building protection are used:
Lightning Rod (simple rod or with triggering system)
The lightning rod is a metallic capture tip placed at the top of the building. It is earthed by one or more conductors (often copper strips) (see Fig. J12).
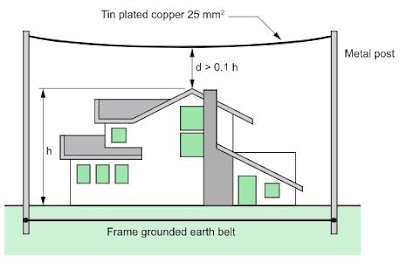
Lightning Rod with Taut Wires: These wires are stretched above the structure to be protected. They are used to protect special structures: rocket launching areas, military applications and protection of high-voltage overhead lines (see Fig. J13).
Fig. J13 – Taut wires
Lightning Conductor with Meshed Cage (Faraday Cage)
This protection involves placing numerous down conductors/tapes symmetrically all around the building. (see Fig. J14).
This type of lightning protection system is used for highly exposed buildings housing very sensitive installations such as computer rooms.
Fig. J14 – Meshed cage (Faraday cage)
Consequences of building protection for the electrical installation's equipment
50% of the lightning current discharged by the building protection system rises back into the earthing networks of the electrical installation (see Fig. J15): the potential rise of the frames very frequently exceeds the insulation withstand capability of the conductors in the various networks (LV, telecommunications, video cable, etc.).
Moreover, the flow of current through the down-conductors generates induced overvoltages in the electrical installation.
As a consequence, the building protection system does not protect the electrical installation: it is therefore compulsory to provide for an electrical installation protection system.
Fig. J15 – Direct lightning back current
This page was last edited on 20 December 2019, at 17:50.
About this wiki
The Electrical Installation Guide is now available here as a wiki (Electrical Installation Wiki). This wiki is a collaborative platform, brought to you by Schneider Electric: our experts are continuously improving its content, as they were doing for the guide. Collaboration to this wiki is also open to all.







কোন মন্তব্য নেই